Abstract:
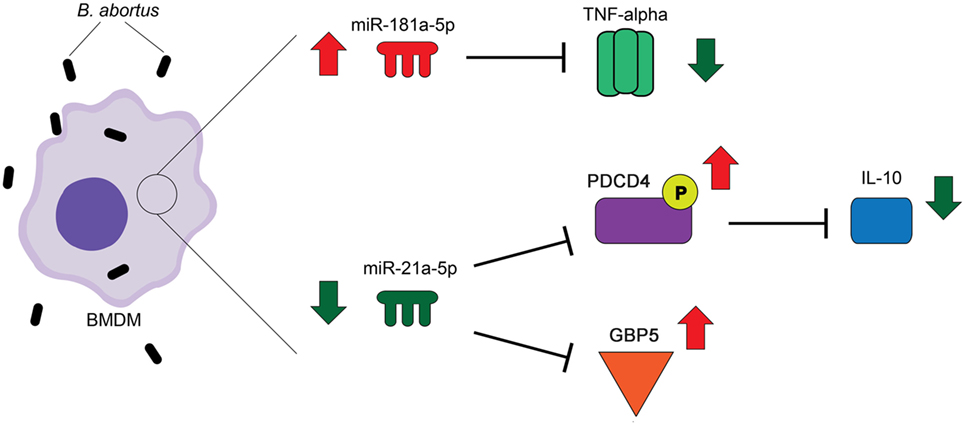
Brucella abortus is a Gram-negative intracellular bacterium that causes a worldwide zoonosis termed brucellosis, which is characterized as a debilitating infection with serious clinical manifestations leading to severe complications. In spite of great advances in studies involving host–B. abortus interactions, there are many gaps related to B. abortus modulation of the host immune response through regulatory mechanisms. Here, we deep sequenced small RNAs from bone marrow-derived macrophages infected with B. abortus, identifying 69 microRNAs (miRNAs) that were differentially expressed during infection. We further validated the expression of four upregulated and five downregulated miRNAs during infection in vitro that displayed the same profile in spleens from infected mice at 1, 3, or 6 days post-infection. Among these miRNAs, mmu-miR-181a-5p (upregulated) or mmu-miR-21a-5p (downregulated) were selected for further analysis. First, we determined that changes in the expression of both miRNAs induced by infection were dependent on the adaptor molecule MyD88. Furthermore, evaluating putative targets of mmu-miR-181a-5p, we demonstrated this miRNA negatively regulates TNF-α expression following Brucella infection. By contrast, miR-21a-5p targets included a negative regulator of IL-10, programmed cell death protein 4, and several guanylate-binding proteins (GBPs). As a result, during infection, miR-21a-5p led to upregulation of IL-10 expression and downregulation of GBP5 in macrophages infected with Brucella. Since GBP5 and IL-10 are important molecules involved in host control of Brucella infection, we decided to investigate the role of mmu-miR-21a-5p in bacterial replication in macrophages. We observed that treating macrophages with a mmu-miR-21a-5p mimic enhanced bacterial growth, whereas transfection of its inhibitor reduced Brucella load in macrophages. Taken together, the results indicate that downregulation of mmu-miR-21a-5p induced by infection increases GBP5 levels and decreases IL-10 expression thus contributing to bacterial control in host cells.
Figure: